Published on: December 18, 2022
Written by Liam Jaxon / Fact-checked by David Rowan
Selecting the right gauge wire for a boat battery is essential for safety and efficiency. Typically, a 6-gauge marine wire is recommended for most applications.
When it comes to wiring a boat, the choice of wire gauge is not just a matter of preference but a critical decision impacting the boat’s electrical system’s safety and functionality. The gauge of wire used for a boat battery plays a pivotal role in ensuring adequate power supply and preventing potential hazards. For general purposes, a 6-gauge marine wire is often suitable, providing a balance between conductivity and durability.
For specific applications, such as boat accessories or battery relocation, the wire gauge might vary. Accessories often require different wire sizes depending on their power needs. A boat battery cable size calculator can be an invaluable tool in these instances, helping to determine the appropriate wire gauge for each unique setup. For instance, a 4-gauge marine wire might be ideal for high-power accessories or systems.
In the context of outboard motors, the wire gauge is equally significant. For an outboard starter, especially in larger engines like a Mercury outboard, the battery cable size needs to be sufficient to handle the starter’s high current demand. Often, a thicker gauge wire, such as a 4 or 6 gauge, is necessary to ensure reliable performance and prevent voltage drops.
Marine battery cables, specifically designed for the marine environment, offer enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion, factors crucial in maintaining the longevity and efficiency of a boat’s electrical system.
For a more detailed understanding of the appropriate wire gauge for different boat applications, including battery relocation and specific outboard models, reading the full article below is recommended. This comprehensive guide provides insights and practical advice to ensure your boat’s electrical system is both safe and optimally configured.
Gauge Guide for Boat Batteries – Essential Wiring Insights
Wire Gauge and Its Importance in Boating
The Basics of Wire Gauge
Let’s start with the basics: wire gauge is a measure of a wire’s diameter. It might sound simple, but it’s a big deal in the boating world. The thickness of the wire affects how much current it can safely carry. Think of it like a water pipe – the wider it is, the more water (or in this case, electricity) it can handle without any issues.
Why Correct Wire Gauge Matters for Boat Batteries
Choosing the right wire gauge for your boat’s battery isn’t just a technicality; it’s about safety and efficiency. A wire that’s too thin can overheat, leading to dangerous situations. Plus, the wrong gauge can mean your boat’s battery won’t perform as well, leaving you in the lurch when you need power the most.
Factors Influencing Wire Gauge Selection for Boat Batteries
Power Requirements of the Boat
The first thing to consider is how much power your boat needs. Bigger boats with more gadgets need thicker wires to handle the load. It’s like needing a bigger fuel line for a larger engine – more power requires a bigger pathway.
Length of the Wiring Run
Distance matters too. The longer the wire, the larger the gauge should be. This is because electricity loses strength over distance. So, for longer wiring runs, you need a beefier wire to ensure enough power gets to where it’s needed.
Voltage Drop Considerations
Voltage drop is a sneaky issue. It’s the loss of voltage as electricity travels along the wire. To keep this to a minimum, especially in critical systems like your boat’s battery, picking the right wire gauge is key. It’s all about keeping the power strong and steady.
Comparing Different Wire Gauges for Boat Batteries
Wire Gauge vs. Current Carrying Capacity
| Wire Gauge | Max Current (Amps) |
| 6 Gauge | 120 Amps |
| 8 Gauge | 80 Amps |
| 10 Gauge | 60 Amps |
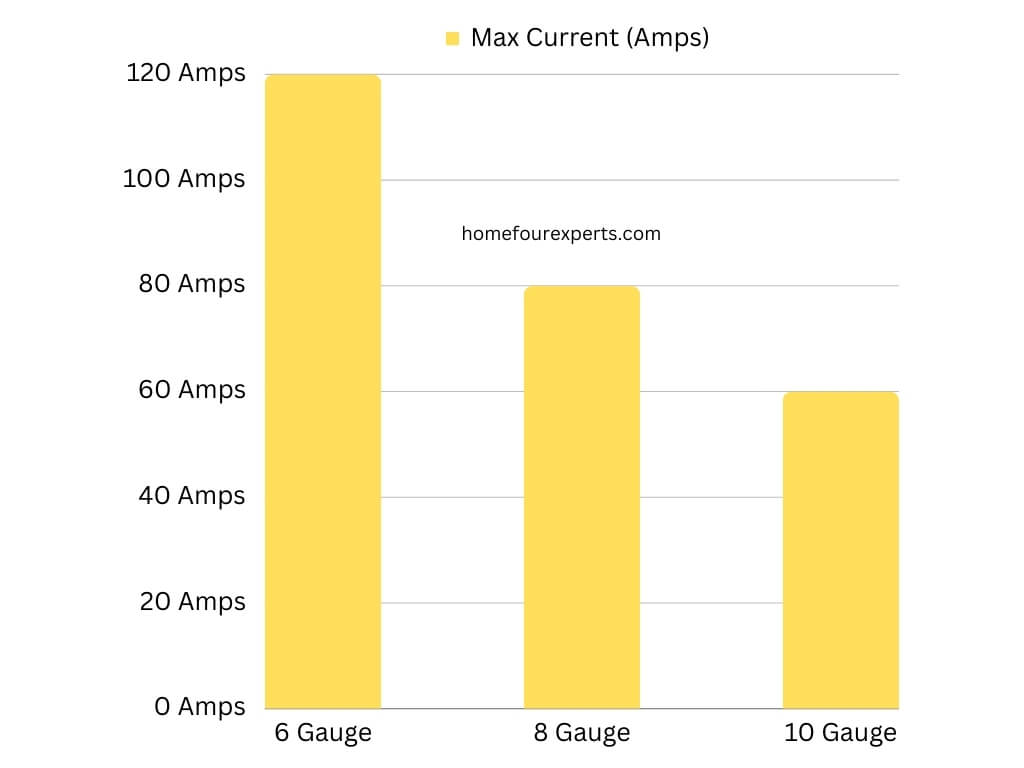
This table shows how different wire gauges can handle different amounts of current. It’s a quick guide to see what each wire size can safely carry.
Pros and Cons of Common Gauges (6, 8, 10 Gauge)
Each wire gauge has its place. A 6-gauge wire is great for high-power needs but can be overkill for smaller systems. An 8-gauge strikes a balance, while a 10-gauge is perfect for lighter loads. It’s all about matching the wire to the job.
Special Considerations for High-Demand Systems
For systems that demand a lot of power, like high-end audio or advanced navigation equipment, going with a thicker gauge is a smart move. It ensures these power-hungry devices get the juice they need without any hiccups.
Wire Gauge Recommendations for Specific Boat Applications
Standard Boat Battery Setups
For most boats, a 6-gauge wire is a solid choice for the main battery connections. It’s thick enough to handle the load but not so bulky that it’s hard to work with.
High-Power Accessories and Electronics
When you’re adding accessories like a powerful sound system or extra lighting, you might need to step up the wire gauge. This ensures these additions work smoothly and don’t strain your boat’s electrical system.
Recommended Wire Gauge for Various Boat Accessories
| Accessory | Recommended Wire Gauge |
| Basic Lighting | 10 Gauge |
| Sound System | 8 Gauge |
| Additional Batteries | 6 Gauge |
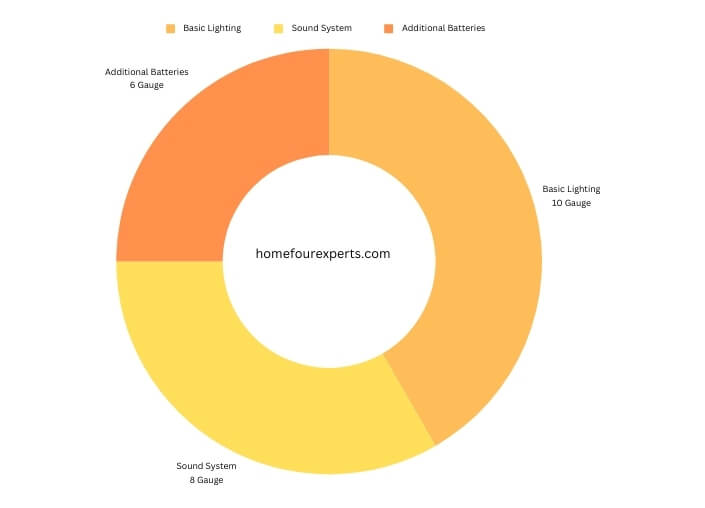
This table helps you match the right wire gauge to different boat accessories. It’s a handy reference to make sure everything runs without a hitch.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Marine Grade Wire Standards
Marine grade wires are built to handle the harsh conditions at sea. They’re resistant to moisture, salt, and temperature changes. Using the right type of wire is just as important as using the right gauge.
Tips for Safe Electrical Installations on Boats
Safety first! Always ensure connections are tight and protected from the elements. Use heat shrink tubing and quality connectors to prevent corrosion and short circuits. It’s all about keeping things shipshape and seaworthy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Wire Selection
One big mistake is underestimating your boat’s power needs and choosing a wire that’s too thin. Also, don’t forget to factor in the length of the wire run – it’s a crucial part of the equation.
Installation Tips and Techniques
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a Boat Battery
Wiring a boat battery isn’t rocket science, but it does require care. Start by disconnecting the power, then measure and cut your wires. Connect them securely, ensuring there’s no strain on the connections. Finally, test everything to make sure it’s working as it should.
Tools and Materials Needed for Proper Installation
You’ll need a few basic tools: wire cutters, strippers, crimpers, and a multimeter. Also, make sure you have marine-grade wire, connectors, and heat shrink tubing. These tools and materials will help you do the job right.
Wire Gauge and Corresponding Stripping and Crimping Tools
| Wire Gauge | Stripping Tool Size | Crimping Tool Size |
| 6 Gauge | Large | Large |
| 8 Gauge | Medium | Medium |
| 10 Gauge | Small | Small |
This table shows which tools work best with different wire gauges. Using the right tools makes the installation smoother and safer.
FAQs
Can Different Wire Gauges Be Used Together?
Yes, different wire gauges can be used together in a boat’s electrical system, but it requires careful planning. The key is to ensure that each wire can handle its specific load. For instance, a thicker wire from the battery can branch into thinner wires for less demanding applications.
It’s vital to never overload a thinner wire beyond its capacity. This approach can be useful for distributing power efficiently across various systems on the boat. Always ensure that connections between different gauges are secure and well-insulated to prevent any electrical hazards.
What Is the Impact of Wire Gauge on Battery Charging?
The wire gauge can significantly impact the efficiency of battery charging. A wire that’s too thin for the charging current can cause resistance, leading to slower charging times and even heat buildup, which is a safety hazard. On the other hand, a wire that’s adequately sized for the charger’s output will facilitate efficient charging, ensuring that the battery charges quickly and safely. It’s essential to match the wire gauge with the charger’s output specifications to maintain an efficient and safe charging system for your boat’s battery.
Does Wire Gauge Affect the Lifespan of a Boat Battery?
Indirectly, the wire gauge can affect the lifespan of a boat battery. Using an inappropriately thin wire can lead to voltage drops and inefficient charging, which can strain the battery. Over time, this strain can reduce the battery’s overall lifespan. A correctly sized wire ensures that the battery receives the right amount of power without overcharging or undercharging, thereby maintaining the battery’s health and potentially extending its lifespan. Consistent and efficient power delivery is key to maximizing the longevity of your boat’s battery.
How Does Wire Insulation Type Affect Gauge Choice?
The type of insulation on a wire plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate gauge for a boat battery. Different insulation materials can withstand varying degrees of temperature and environmental stress. In marine environments, where wires are exposed to moisture, salt, and temperature fluctuations, choosing a wire with robust, marine-grade insulation is essential. This might mean opting for a slightly larger gauge to accommodate the thicker, more durable insulation, ensuring the wire remains protected against the harsh marine conditions.
Is There a Difference Between AC and DC Wire Gauge Requirements?
Yes, there is a difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) wire gauge requirements. AC systems, often found in shore power connections, can experience higher levels of current and voltage fluctuations compared to DC systems, which are typically used in boat batteries and electronics. As a result, AC systems may require thicker wires to handle these fluctuations safely. When selecting wire gauge for AC systems, considering both the current and potential voltage changes is important to ensure safety and efficiency.
How Does Wire Gauge Selection Vary for Different Boat Sizes?
The size of the boat can influence wire gauge selection. Larger boats with more complex electrical systems and longer wire runs typically require thicker wires to ensure adequate power distribution and to minimize voltage drops. In contrast, smaller boats with simpler systems and shorter wiring can often use thinner wires. It’s essential to consider the total electrical load and the length of the wire runs when choosing the wire gauge, regardless of the boat size, to ensure safe and efficient operation of the boat’s electrical system.
What Are the Risks of Using an Undersized Wire Gauge?
Using an undersized wire gauge for a boat battery is risky and can lead to several problems.
- It can cause excessive heat buildup due to resistance, which is a significant fire hazard.
- An undersized wire can lead to voltage drops, meaning the battery and connected equipment may not receive sufficient power, leading to poor performance and potential damage to sensitive electronics.
- Consistently overloading a thin wire can lead to its degradation and failure, posing safety risks and necessitating costly repairs. It’s crucial to select the appropriate wire gauge to avoid these risks.
In this guide, we’ve walked through the essentials of choosing the right wire gauge for your boat’s battery. From understanding the basics to installing the wires correctly, it’s all about matching the wire to the power needs, ensuring safety, and using the right tools. Keep these tips in mind, and you’ll have a boat that’s not only fun but also safe and reliable.
About This Writer

Hi, I am responsible for the 'Homeowners Power Solutions' category. My name is Liam Jaxon and a licensed technician with 7 years of experience in vehicle batteries, electrical gadgets, and home appliances. My working experience in different residential & light commercial electrical sectors and the automobile industry helped to acquire vast knowledge in this industry.